Fun Tips About What Is The Root Area Of A Thread
Internal Threads Vs External At Rose Jordan Blog
Delving into the Depths
1. What's the Big Deal with Thread Root Area?
Ever wondered what makes a screw or bolt so strong? It's not just the shiny metal, my friend. A critical factor is something called the "root area of a thread." Now, that might sound like something only engineers care about, but it actually affects anyone who's ever built anything, from a simple bookshelf to a complex machine. So, buckle up; we're about to dive into the world of threads!
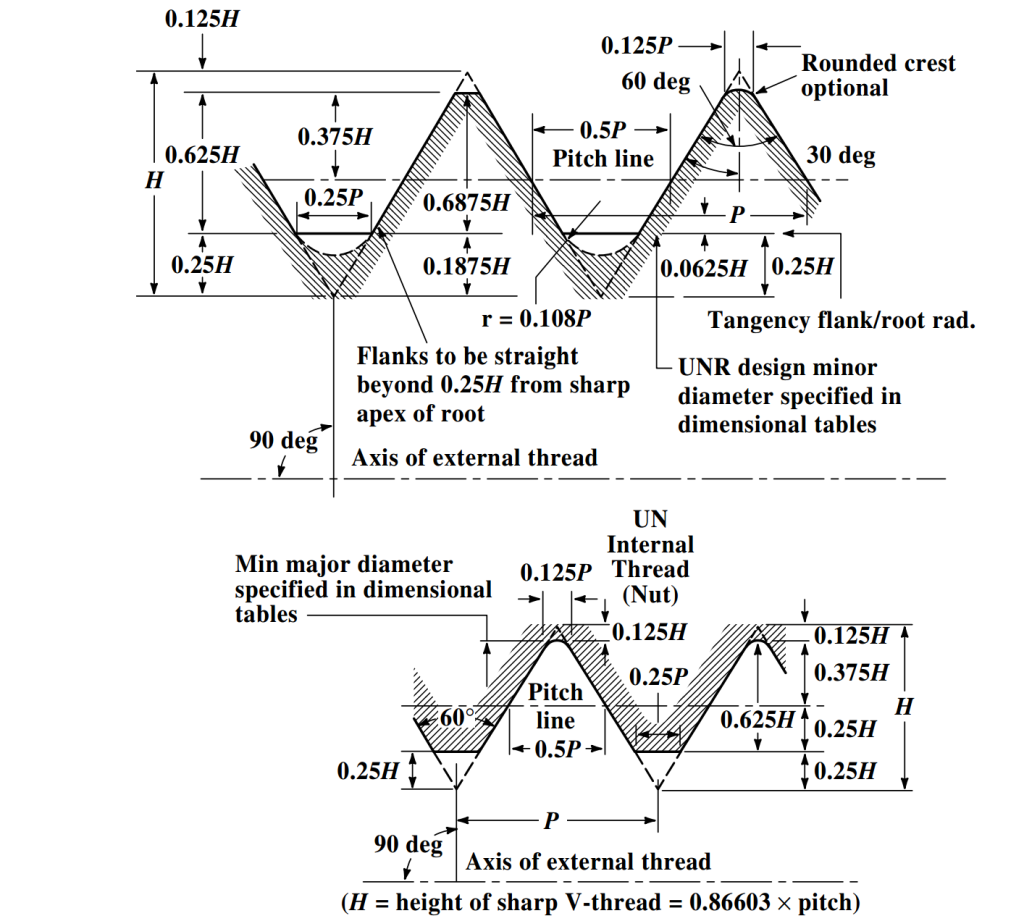
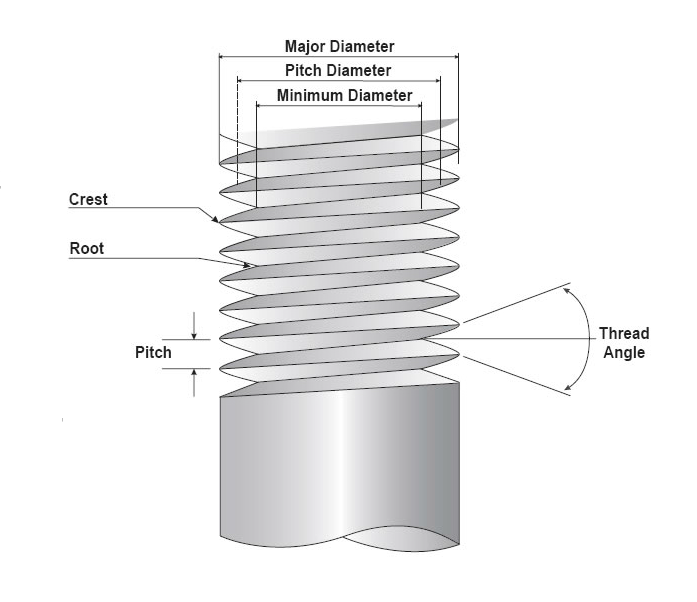
Think of a screw thread as a tiny, spiraling ramp. The root area is essentially the smallest cross-sectional area of that ramp, measured at the very base of the thread where it meets the core of the screw. This area is super important because it determines how much tensile stress the screw can withstand before it decides to call it quits and break. Imagine trying to lift something heavy with a rope that's frayed in the middle. That frayed part is your weak point, just like the root area of a thread.
Why is this area the weakest link? Because all the force trying to pull the screw apart is concentrated there. The smaller the root area, the less force it can handle. Thats why understanding and calculating this area is so crucial in engineering design. It helps engineers choose the right size and type of screw for the job, ensuring everything stays firmly together.
You might be thinking, "Okay, but how does this affect me?" Well, have you ever had a screw shear off while assembling furniture? Or maybe a bolt broke on your car? Chances are, the stress exceeded the capacity of the screw, which has a lot to do with root area. Understanding this concept, even on a basic level, can help you make better choices when selecting fasteners for your own projects. No one wants a wobbly bookshelf!

Calculating the Root Area
2. The Formula — Let's Break It Down
Alright, let's talk about numbers! Don't worry, we're not going to get too bogged down in complicated equations. The root area of a thread isn't something you typically calculate by hand these days (thank you, computers!), but knowing the general formula helps understand the factors involved. A simplified formula looks something like this: Root Area (dr/2)2 , where dr is the root diameter.
So, what's the root diameter? It's simply the diameter of the screw measured at the bottom of the threads. Think of it as the skinny part of the screw core. You need to know this measurement to plug it into the formula. Fortunately, this info is usually available in fastener specifications or engineering tables. No need to whip out your calipers and start measuring microscopic details (unless you're into that kind of thing, no judgement!).
This calculation is crucial for engineers as they determine the stress area* of a fastener, which is related to the root area. The stress area is used to calculate the tensile stress a fastener experiences under load. If the calculated stress exceeds the fastener's tensile strength (also readily available in its specs), then that fastener will fail! Hence, choosing the right size fastener with the proper root area ensures a secure and reliable connection.
However, the real math magic happens in engineering software and calculators. These tools take into account various factors like thread pitch, material properties, and safety factors to give more accurate results. But, understanding the basic principles, like the importance of the root area, is always a good idea. Its like knowing a pinch of salt can make or break a meal, and knowing it before you're serving a flavorless dish to guests is always better!
Metric Threads Per Inch Chart
Why Root Area Matters
3. From Bridges to Bikes — The Importance of Secure Fasteners
The root area of a thread isn't just a theoretical concept; it has profound implications in the real world. Think about large-scale infrastructure projects like bridges and skyscrapers. These structures rely on thousands, if not millions, of fasteners. If the root area of those fasteners is underestimated, the consequences could be catastrophic. Imagine a bridge collapsing because the bolts couldn't handle the stress — scary, right?
Even in everyday applications, the root area is crucial. Consider the humble bicycle. Every bolt and screw plays a vital role in keeping it together. The stem bolts, for instance, hold the handlebars in place. If those bolts were to fail due to an inadequate root area, the rider could lose control. Suddenly, that seemingly insignificant detail becomes a matter of safety.
The automotive industry is another area where root area calculations are paramount. From engine components to suspension systems, every fastener must be able to withstand extreme stress and vibration. An engine bolt with an insufficient root area could break under the heat and pressure, leading to engine failure. This not only causes inconvenience but also poses a safety risk.
And lets not forget aerospace engineering! The requirements for fasteners in aircraft are extraordinarily high. The slightest miscalculation in root area could lead to structural failure at high altitudes. This is why stringent quality control and precise engineering are essential in the aviation industry. So, next time youre on a plane, spare a thought for the engineers who carefully calculated the root area of every single fastener!

Factors Affecting Thread Root Area
4. More Than Just Size
The root area of a thread isn't just determined by its basic dimensions. Several other factors can influence its effective strength. One of the most important is the material of the fastener. A high-strength alloy steel will have a significantly higher tensile strength than a low-carbon steel, even if the root area is the same.
The manufacturing process also plays a role. Threads can be formed by cutting or rolling. Rolled threads generally have a higher root area strength because the process work-hardens the material, making it stronger. Cut threads, on the other hand, can weaken the material, reducing the effective root area.
The thread pitch, which is the distance between adjacent threads, also affects the root area. A finer pitch generally results in a larger root area for a given diameter, but it can also make the threads more susceptible to stripping. Finding the right balance between pitch and root area is a key aspect of fastener design.
Finally, environmental factors such as temperature and corrosion can affect the root area. High temperatures can weaken the metal, reducing its strength. Corrosion can eat away at the threads, effectively decreasing the root area over time. This is why choosing the right material and applying protective coatings are essential for fasteners that will be exposed to harsh environments. In short, it's a complex interplay of factors that must all be carefully considered.
[Solved] 2. A / DIAMETER BOLT, WAVING AT THE ROOT OF
Choosing the Right Fastener
5. Matching the Screw to the Job
So, how do you choose the right fastener for your project? Well, first, consider the load that the fastener will need to bear. Estimate the tensile force that will be applied and then consult engineering tables or online calculators to determine the appropriate fastener size and material. Remember, it's always better to err on the side of caution and choose a fastener that's slightly stronger than you think you need.
Next, think about the environment. Will the fastener be exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures? If so, choose a corrosion-resistant material like stainless steel or consider applying a protective coating. Also, think about the type of material you're fastening together. Different materials require different types of threads. For example, wood screws are designed specifically for use in wood, while machine screws are better suited for metal.
Dont skimp on quality! It might be tempting to save a few bucks by buying the cheapest fasteners you can find, but that's often a false economy. Low-quality fasteners are more likely to fail, which can lead to costly repairs or even dangerous situations. Invest in reputable brands that adhere to strict quality control standards. Your safety and the integrity of your project depend on it.
In doubt, consult an expert. If you're working on a critical application, such as building a deck or repairing a vehicle, don't hesitate to seek professional advice. A qualified engineer or experienced tradesperson can help you select the right fasteners and ensure that they are installed correctly. Remember, proper installation is just as important as choosing the right fastener in the first place.

3D Printed Threads Model Them In Fusion 360 Practical, 57 OFF
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered!
Okay, so you've learned about the root area of a thread. But you probably still have some questions. Let's tackle some of the most common ones:
Q: What happens if the root area is too small?
A: If the root area is too small, the fastener will be more likely to fail under stress. It could break, shear, or strip, leading to a weakened connection or even a catastrophic failure.
Q: How can I find the root diameter of a thread?
A: The root diameter is usually listed in the fastener's specifications or engineering tables. You can also find it using online calculators or by measuring it directly with calipers (though that's best left to the pros!).
Q: Is the root area the same as the tensile stress area?
A: Not exactly. The tensile stress area is a calculated value that takes into account the root area and other factors, such as the thread pitch. It's used to determine the tensile stress that a fastener can withstand.