Brilliant Tips About What Is A Good PPM For Quality

PPT Reliability & Responsiveness Meeting Your Shipping Needs
Parts Per Million and the Pursuit of Quality
1. Understanding PPM in the Realm of Quality Control
Ever heard someone throw around the term "PPM" and felt like you were suddenly transported back to chemistry class? Well, relax! PPM, or Parts Per Million, isn't just for lab coats and beakers. It's a crucial metric in various industries, from manufacturing to environmental science, and it plays a vital role in assessing quality. Think of it as a way to measure how many 'bad apples' there are in a really, really big barrel of apples. A "good" PPM means fewer bad apples, which translates to higher quality!
So, what exactly is Parts Per Million? It's simply a way of expressing a very, very dilute concentration of a substance. Imagine you have a million marbles, and only one of them is red. That's 1 PPM of red marbles. In the context of quality, we're usually talking about defective parts, contaminants, or anything else that shouldn't be there. The lower the PPM, the better, generally speaking.
But heres the kicker: a good PPM isn't a one-size-fits-all kind of deal. Whats acceptable in one industry might be completely unacceptable in another. Think about it: the acceptable level of impurities in drinking water is going to be drastically different from the acceptable level of defects in, say, plastic toys. It all boils down to risk assessment and what's considered safe and reasonable.
Ultimately, the significance of PPM lies in its capacity to transform intricate measurements into easily digestible figures. Instead of grappling with extremely small decimals or cumbersome scientific notation, PPM offers a more intuitive method for assessing and communicating levels of impurities or defects. This clarity is invaluable for decision-makers who depend on accurate information to make informed judgments.
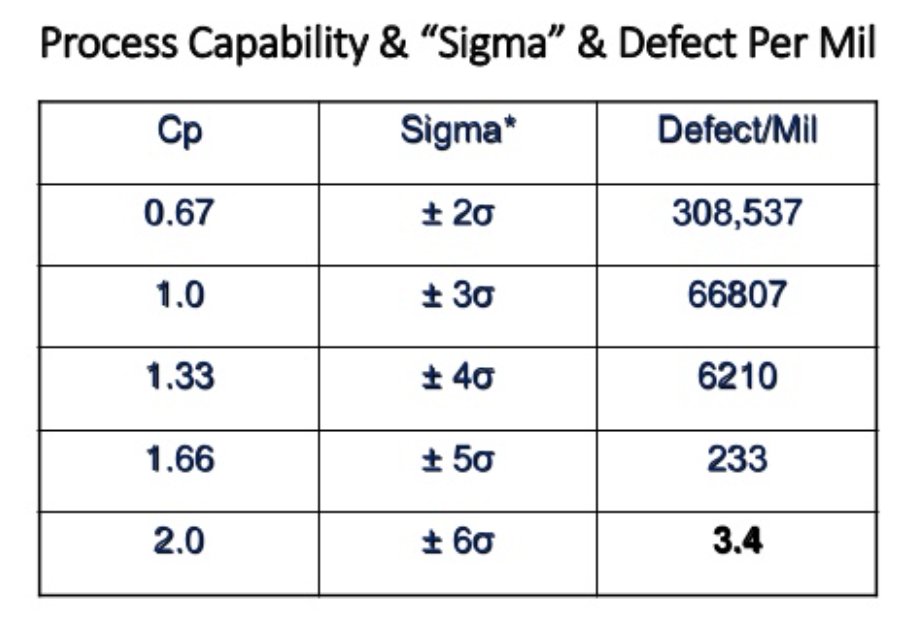
Six Sigma CPK, Sigma, DPPM
Industry Standards
2. Navigating the PPM Landscape Across Different Sectors
Now, let's dive into some specific examples. In the automotive industry, for instance, a high PPM of defective parts can lead to recalls, safety issues, and a whole lot of unhappy customers. Therefore, automotive manufacturers strive for extremely low PPM levels, often aiming for single-digit or even sub-PPM figures. Their focus is on meticulously refining production processes and quality assurance protocols to minimize the occurrence of any defects.
On the flip side, in the food and beverage industry, PPM might be used to measure the concentration of certain additives or contaminants. While zero PPM is always the ideal goal for contaminants, some additives are necessary for preservation or flavor. In these cases, regulations set acceptable PPM levels that are deemed safe for consumption. These levels are typically established through extensive scientific research and risk assessment.
The pharmaceutical industry operates under some of the most stringent PPM standards globally. Every step, from ingredient sourcing to the final packaging of medication, is subject to careful oversight to prevent even tiny changes that could impact the efficiency or safety of products. These efforts are driven by severe ethical and legal duties to ensure the wellbeing of patients who rely on their products.
And then theres the electronics industry, where even microscopic defects can wreak havoc. A tiny speck of dust on a microchip can render it useless. Therefore, electronics manufacturers invest heavily in cleanroom environments and advanced testing equipment to minimize PPM and ensure the reliability of their products. The level of scrutiny and preventative measures taken in this industry are truly astonishing.

Factors Influencing Your Ideal PPM Target
3. Deciding on Your Optimal PPM Threshold
Several factors play a part in determining what constitutes a "good" PPM for your specific situation. One of the biggest is the cost of failure. If a defect is going to cost a lot of money, time, or even lives, you'll want to aim for a very low PPM. Think about the difference between a faulty stapler and a faulty airplane part! The consequences are vastly different, and so should be the acceptable PPM.
Another factor is the complexity of the product or process. More complex processes are inherently more prone to errors, which can lead to higher PPM levels. So, if you're dealing with a particularly intricate operation, you might need to accept a slightly higher PPM, but you'll also need to invest more in quality control to keep it as low as possible.
Regulatory requirements also play a huge role. Many industries are subject to strict regulations that dictate acceptable PPM levels for certain substances or defects. Failing to meet these requirements can result in hefty fines, legal action, or even the shutdown of your operations. So, it's crucial to be aware of and comply with all applicable regulations.
Lastly, customer expectations can influence your PPM targets. Even if you're meeting all regulatory requirements, customers may still have certain expectations about the quality of your products or services. If you want to maintain a good reputation and keep your customers happy, you'll need to strive for a PPM that meets or exceeds their expectations. Listen to their feedback, address their concerns, and continuously improve your quality control processes.
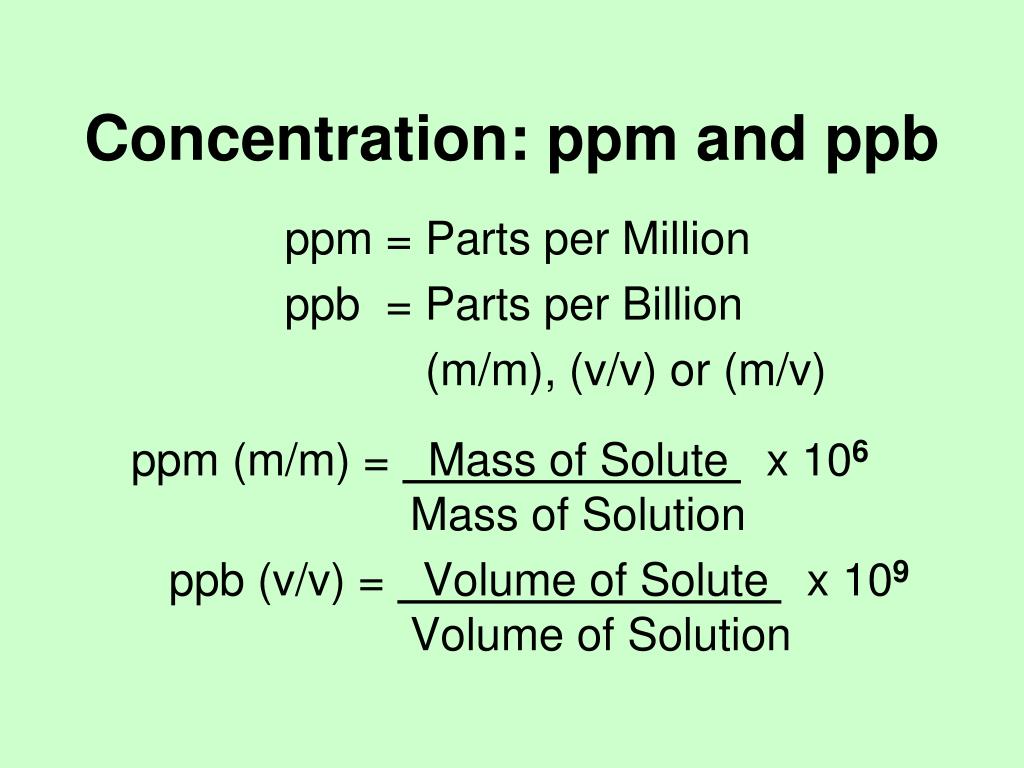
How To Calculate Ppm Formula Image U
Achieving and Maintaining a Low PPM
4. Proven Methods for Enhancing Quality and Reducing PPM
Okay, so you know what PPM is, why it matters, and how to determine your ideal target. But how do you actually achieve a low PPM? One of the most effective strategies is to implement robust quality control processes. This includes everything from incoming materials inspection to in-process testing to final product verification. The goal is to identify and eliminate defects as early as possible in the production cycle.
Another key strategy is to invest in employee training. Your employees are the front lines of quality control, and they need to be properly trained to identify and report potential defects. Provide them with the tools and knowledge they need to do their jobs effectively, and empower them to take ownership of quality.
Statistical Process Control (SPC) can also be a powerful tool for reducing PPM. SPC involves using statistical methods to monitor and control processes, identify trends, and detect potential problems before they lead to defects. By implementing SPC, you can proactively manage your processes and prevent PPM from creeping up.
Don't underestimate the power of continuous improvement. Quality is not a destination; it's a journey. Regularly review your processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to drive down PPM. Encourage feedback from employees, customers, and suppliers, and use that feedback to make your quality control processes even better. The relentless pursuit of improvement is key to achieving and maintaining a low PPM over the long term.

The Future of PPM
5. Looking Ahead
The world of PPM is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and increasing customer expectations. One of the most exciting trends is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in quality control. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential defects, allowing manufacturers to take proactive measures to prevent them.
Another promising technology is advanced sensor technology. Sophisticated sensors can now detect even the tiniest imperfections in materials and products, allowing for more precise and accurate quality control. These sensors can be integrated into production lines to provide real-time feedback and automate the inspection process.
Blockchain technology is also starting to make its way into the quality control arena. Blockchain can be used to track and trace materials and products throughout the supply chain, ensuring that they meet quality standards at every step of the process. This can help to prevent counterfeit products from entering the market and improve overall product safety.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect PPM standards to become even more stringent and quality control processes to become even more sophisticated. Companies that embrace these advancements and invest in innovation will be best positioned to meet the challenges of the future and deliver high-quality products and services to their customers. The journey towards zero PPM is an ongoing one, but the rewards are well worth the effort.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. Your Burning PPM Questions Answered
We know you probably still have some questions buzzing around. Lets tackle a few common ones!
7. What's the difference between PPM and PPB (Parts Per Billion)?
Think of it like this: PPM is like one drop of food coloring in a bathtub of water. PPB is like one drop of food coloring in an Olympic-sized swimming pool! PPB is a much smaller concentration than PPM. So, 1 PPM is equal to 1,000 PPB.
8. Is a lower PPM always better?
Generally, yes. But it depends on the context! As we discussed, some substances are necessary at certain levels. The key is to stay within acceptable regulatory limits and meet customer expectations.
9. How can I measure PPM in my own business?
That depends on what you're measuring! You might need specialized equipment, lab testing, or statistical analysis. Consider consulting with a quality control expert to determine the best approach for your specific needs.