First Class Tips About What Is A Remote Power Source

Unplugged and Unbound
1. Understanding the Basics of Remote Power
Ever find yourself staring at a device, wishing you could just snip that pesky power cord and be done with it? Well, that's the essence of what we're talking about today: remote power sources. But it's more than just cutting cords (please don't do that!). It's about providing electricity to a device without a physical connection to the traditional power grid. Think of it as giving your gadgets the freedom to roam!
So, what is a remote power source in a nutshell? It's any method of delivering electricity to a device without a direct cable connection. This could involve batteries, solar panels, wireless power transfer, or even more exotic technologies. The key is that it untethers the device from the wall socket, opening up a world of possibilities for portability and placement.
The need for remote power is driven by our increasingly mobile and wireless world. We want our devices to go where we go, without being tethered to a specific location. From smartphones and laptops to drones and electric vehicles, the demand for convenient and reliable remote power is only growing. And honestly, who doesn't appreciate the convenience of not having to hunt for an outlet?
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) is also a huge factor. Imagine thousands of sensors scattered across a field, monitoring soil conditions. Running power cables to each of them would be a logistical nightmare! Remote power sources offer a practical and cost-effective solution for powering these distributed networks, making data collection and analysis much simpler.

Different Flavors of Untethered Energy
2. Diving Deeper into Remote Power Technologies
Alright, now that we know what remote power sources are, let's explore some of the most common technologies that make it all possible. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, so choosing the right one depends on the specific application.
Batteries: The old reliable. From tiny coin cells to massive lithium-ion packs, batteries are the workhorses of remote power. They're portable, relatively inexpensive, and readily available. However, they need to be recharged or replaced periodically, which can be a drawback in some situations. Plus, battery disposal is an environmental concern that we all need to be mindful of.
Solar Power: Harnessing the power of the sun! Solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity. They're a clean and sustainable option, perfect for outdoor applications like solar-powered lights, charging stations, and even entire homes. The downside? They rely on sunlight, so their performance can vary depending on weather conditions and time of day.
Wireless Power Transfer: This one's straight out of science fiction (well, almost!). Wireless power transfer uses electromagnetic fields to transmit electricity through the air. Think of it as charging your phone without plugging it in. While still under development for large-scale applications, it holds tremendous potential for powering devices remotely and conveniently.
Other Options: There are other more specialized methods, such as fuel cells (which use chemical reactions to generate electricity) and thermoelectric generators (which convert heat into electricity). These technologies are often used in niche applications where other power sources aren't practical.

Solar Energy Model (renewable Model) Making Using Cardboard And
The Upsides and Downsides
3. Considering the Advantages and Disadvantages
Like anything in life, remote power sources come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Before you jump on the wireless bandwagon, it's important to weigh the pros and cons to see if it's the right fit for your needs.
The Good Stuff: The biggest advantage, of course, is mobility and flexibility. Remote power frees devices from the constraints of power cords, allowing them to be used anywhere, anytime. This is especially important for applications like mobile devices, drones, and remote sensors. Plus, it can simplify installation and reduce clutter, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
The Not-So-Good Stuff: One of the main drawbacks is limited power capacity. Batteries, for example, can only store a finite amount of energy, so they need to be recharged or replaced. Solar panels are dependent on sunlight. Wireless power transfer often has lower efficiency than wired connections. And sometimes, remote power sources can be more expensive than traditional wired power.
Real-World Considerations: You also need to consider factors like environmental impact. Battery disposal can be a concern, and the manufacturing process for solar panels and other remote power technologies can have its own environmental footprint. It's important to choose remote power solutions that are sustainable and minimize environmental impact.
The Future is Bright (and Wireless?): Despite the challenges, the benefits of remote power often outweigh the drawbacks, especially as technology continues to improve. As batteries become more energy-dense, solar panels become more efficient, and wireless power transfer becomes more practical, we can expect to see even wider adoption of remote power sources in the years to come.
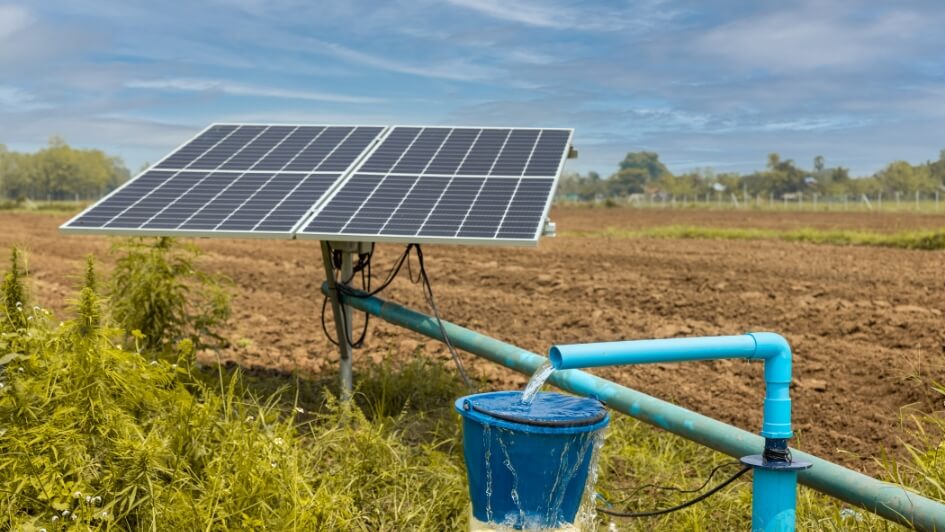

How Distributed Renewable Energy Can Reshape Agriculture For
Applications Galore
4. Exploring Practical Applications
Remote power isn't just a theoretical concept; it's already revolutionizing a wide range of industries and applications. Let's take a look at some examples of where remote power is making a real difference.
Mobile Devices: Smartphones, tablets, laptops — these are the poster children for remote power. Batteries allow us to stay connected and productive on the go, without being tethered to a wall outlet. And wireless charging is making it even more convenient to keep our devices powered up.
Electric Vehicles: The automotive industry is embracing remote power in a big way. Electric cars rely entirely on batteries for propulsion, and wireless charging technology is poised to make charging even easier and more convenient. Imagine simply parking your car over a charging pad and letting it juice up automatically!
IoT Devices: As mentioned earlier, remote power is essential for powering the vast network of IoT devices that are being deployed in various industries. From sensors in agriculture to smart home devices, remote power allows these devices to operate autonomously and collect data without the need for wired connections.
Medical Devices: Remote power is also playing an increasingly important role in healthcare. Pacemakers, insulin pumps, and other implantable medical devices rely on batteries for operation. And wireless power transfer is being explored as a way to recharge these devices without surgery.
Aerospace and Defense: From powering satellites in space to enabling autonomous drones, remote power is critical for many aerospace and defense applications. Solar panels, fuel cells, and batteries are all used to provide reliable power in these demanding environments.
.jpg)
Charging Ahead
5. Peering into the Future of Untethered Energy
The field of remote power is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging all the time. What can we expect to see in the future?
Better Batteries: Researchers are working tirelessly to develop batteries that are more energy-dense, longer-lasting, and safer. Solid-state batteries, for example, are a promising technology that could significantly improve battery performance.
More Efficient Solar Panels: Advances in materials science are leading to solar panels that are more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. Perovskite solar cells, for example, are a new type of solar cell that has the potential to be much cheaper and more efficient than traditional silicon solar cells.
Widespread Wireless Power: Wireless power transfer is becoming more practical and affordable. We can expect to see wireless charging become more commonplace in our homes, offices, and public spaces. Imagine entire rooms that can wirelessly power your devices!
Integration and Intelligence: Remote power sources are becoming more integrated and intelligent. Smart batteries, for example, can communicate with devices to optimize power consumption and extend battery life. And AI-powered energy management systems can help us manage our remote power resources more efficiently.Ultimately, the future of remote power is bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see remote power sources become even more prevalent, reliable, and sustainable.
FAQ
6. Frequently Asked Questions About Remote Power
Still have some questions swirling around? Let's tackle some common queries about remote power sources.
Q: How efficient is wireless power transfer compared to wired charging?
A: Currently, wireless power transfer is generally less efficient than wired charging. Some energy is lost in the transmission process. However, technology is improving, and the gap is narrowing. The convenience factor often outweighs the slight loss in efficiency for many users.
Q: Are there any safety concerns with wireless power transfer?
A: Wireless power transfer systems are designed to be safe for humans and animals. They typically operate at low power levels and use shielding to minimize electromagnetic radiation. However, it's always a good idea to follow the manufacturer's instructions and avoid prolonged exposure to high-power wireless charging devices.
Q: What's the environmental impact of remote power sources?
A: The environmental impact varies depending on the type of remote power source. Batteries can pose environmental concerns due to disposal issues. Solar panels have a cleaner profile during operation, but their manufacturing process can have its own impacts. It's important to choose remote power solutions that are sustainable and minimize environmental footprint.