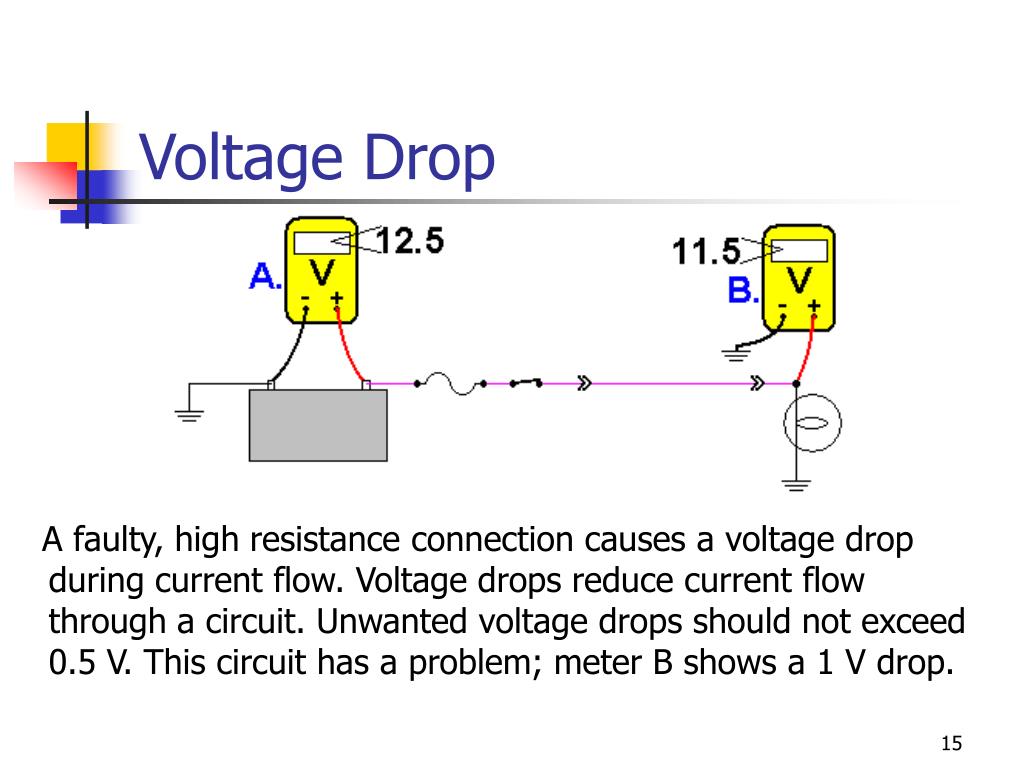
Breathtaking Tips About What Is Meant By Voltage Drop

Understanding Voltage Drop
1. Why Should I Care About Voltage Drop?
Ever noticed your lights dimming when you turn on a power-hungry appliance? Or perhaps your device charges frustratingly slowly? Chances are, you're experiencing the sneaky culprit known as voltage drop. It's a concept that might seem intimidating, but trust me, it's simpler than figuring out your phone's privacy settings. Basically, voltage drop is the reduction in electrical potential along a conductor (like a wire) as current flows through it. Think of it like water flowing through a pipe — the further the water has to travel, the lower the pressure gets at the end. Electrical current behaves similarly, except instead of water pressure, we're talking about voltage!
Now, why does this matter? Well, significant voltage drop can lead to all sorts of problems. Dim lights are just the beginning. It can cause appliances to malfunction, motors to overheat, and electronic devices to perform erratically. In extreme cases, it can even pose a fire hazard. So, understanding and addressing voltage drop is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of your electrical systems. It's not just a theoretical concept; it directly impacts the performance of your gadgets and the safety of your home.
Think of it like this: you wouldn't want to try running a marathon wearing shoes two sizes too small, would you? Your electrical appliances feel the same way when they're not getting the voltage they need. They get tired, underperform, and might even call it quits prematurely. Keeping voltage drop in check is like giving your electronics the comfortable, supportive shoes they need to go the distance.
So, buckle up, because we're about to delve into the world of voltage drop and unravel its mysteries. We'll explore what causes it, how to measure it, and, most importantly, how to prevent it from wreaking havoc on your electrical system. Don't worry, we'll keep it light and avoid any overly technical jargon. After all, who needs another headache?
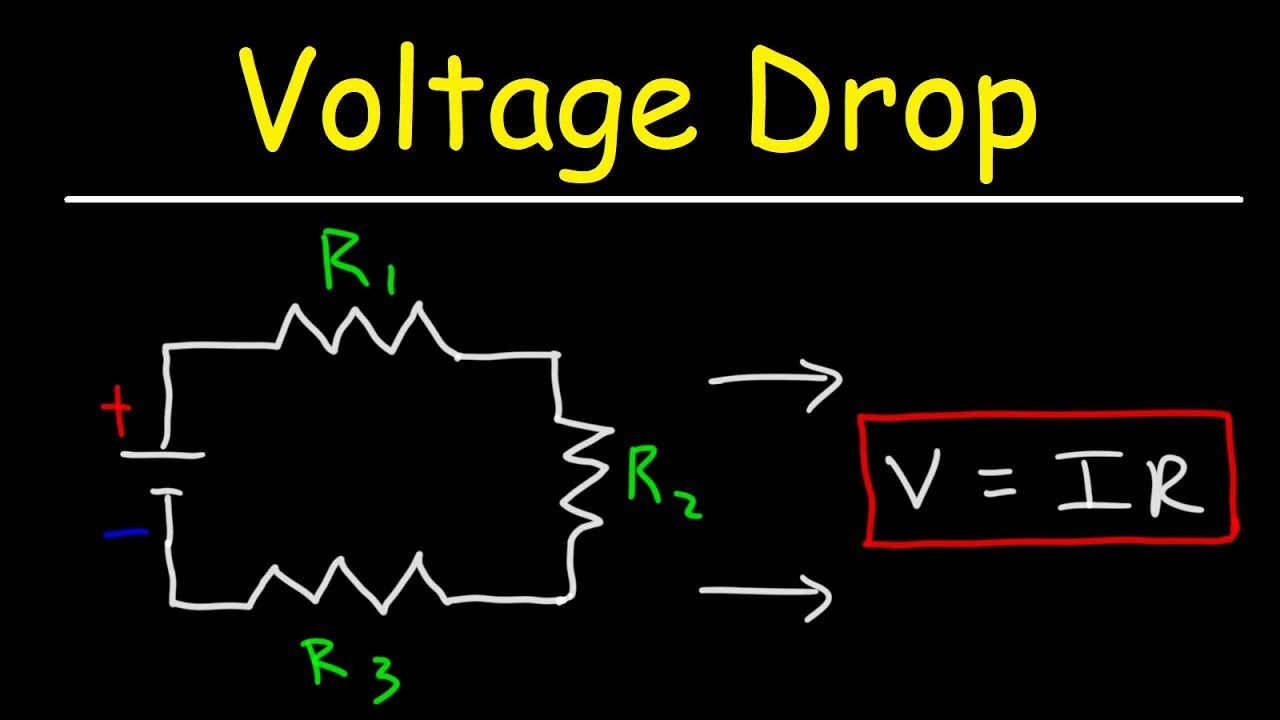
Voltage Drop Essential Guide To Preventing Power Loss Electricove
What Actually Causes Voltage Drop? The Culprits Revealed!
2. Resistance is NOT Futile!
The primary cause of voltage drop is resistance. Every conductor, even a copper wire, offers some resistance to the flow of electrical current. This resistance converts some of the electrical energy into heat, which is why wires can sometimes feel warm to the touch. The greater the resistance, the greater the voltage drop. It's like trying to push a shopping cart through thick mud — you're going to lose some energy along the way.
Several factors influence resistance. The length of the conductor is a big one. A longer wire will have more resistance than a shorter wire of the same gauge. This is because the electrons have to travel further, encountering more obstacles along the way. The gauge (thickness) of the wire also plays a crucial role. A thinner wire has a smaller cross-sectional area, making it more difficult for electrons to flow, resulting in higher resistance. Think of it like trying to squeeze a crowd of people through a narrow doorway — it's going to be much harder than if the doorway was wide.
Another factor is the material of the conductor. Copper is a popular choice for electrical wiring because it has relatively low resistance. Other materials, like aluminum or steel, have higher resistance and will result in greater voltage drop. Also, the temperature of the conductor affects resistance; as temperature increases, resistance tends to increase as well. So, a hot wire will experience more voltage drop than a cold wire.
Finally, connections can also contribute to voltage drop. Loose or corroded connections introduce additional resistance into the circuit. This is why it's important to ensure that all connections are tight and clean. A loose connection is like a pothole in the road — it slows everything down and causes unnecessary wear and tear.

Calculating Voltage Drop
3. Formulas & Calculations (Simplified!)
Okay, I know what you're thinking: "Math? Seriously?" But don't worry, we're not going to dive into complex calculus. Calculating voltage drop can be surprisingly straightforward, especially with a few handy formulas. The most common formula is Ohm's Law: Voltage (V) = Current (I) x Resistance (R). In the context of voltage drop, this translates to the voltage drop across a conductor being equal to the current flowing through it multiplied by the resistance of the conductor.
However, for practical applications, especially when dealing with longer wire runs, we often use a more specific formula that takes into account the wire's length and properties. A simplified version looks something like this: Voltage Drop = (2 x K x I x L) / CM, where K is a constant representing the wire material (usually copper or aluminum), I is the current in amperes, L is the one-way length of the wire in feet, and CM is the circular mils of the wire (a measure of its cross-sectional area). Don't panic about the "circular mils"; you can usually find this information in wire gauge charts or online.
Using these formulas, you can estimate the voltage drop for a given circuit and determine if it's within acceptable limits. Most electrical codes specify maximum allowable voltage drops, typically around 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders. If your calculated voltage drop exceeds these limits, you'll need to take steps to reduce it, such as using a thicker wire or shortening the wire run.
There are also many online voltage drop calculators that can do the math for you. Just plug in the values for current, wire length, wire gauge, and material, and the calculator will spit out the voltage drop. These calculators are a great resource for quickly assessing voltage drop in different scenarios. Remember, knowing how to calculate voltage drop empowers you to design safer and more efficient electrical systems. And who doesn't want that?
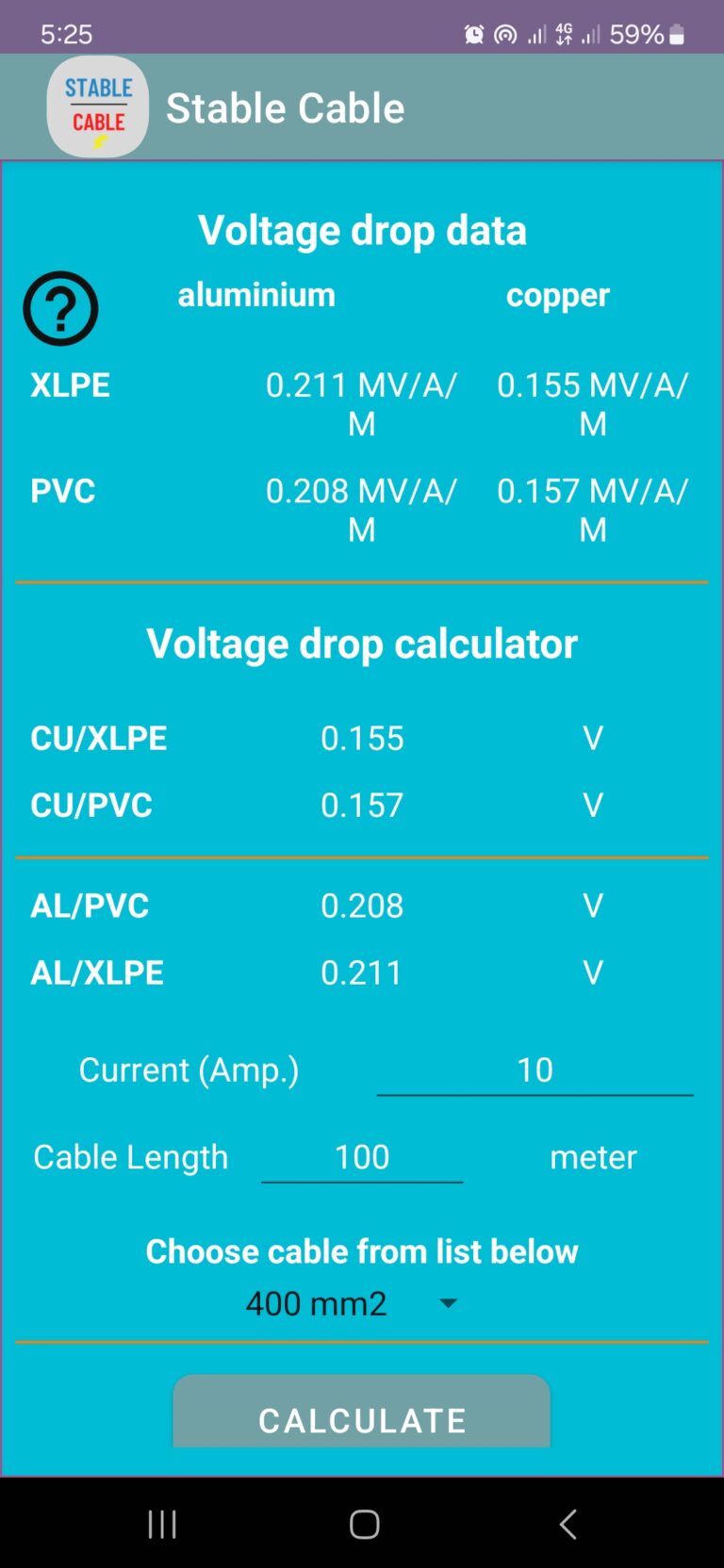
Voltage Drop Causes, Solutions And Calculations
Fixing Voltage Drop
4. Solutions for happy Electricity
So, you've calculated the voltage drop and discovered it's higher than you'd like. Don't despair! There are several ways to combat voltage drop and restore your electrical system to its full potential. One of the most effective solutions is to increase the wire gauge. Remember, thicker wires have lower resistance, so they'll experience less voltage drop. It's like upgrading from a garden hose to a fire hose — more current can flow with less pressure loss.
Another approach is to shorten the wire run. The shorter the distance the current has to travel, the less voltage drop there will be. This might involve relocating the power source or the load closer to each other. Think of it like taking a shortcut — you'll arrive at your destination faster and with less effort. You could also consider using a higher voltage. Since power equals voltage times current, increasing the voltage allows you to deliver the same amount of power with less current, which in turn reduces voltage drop.
Regular maintenance of electrical connections is crucial for preventing voltage drop. Ensure that all connections are tight, clean, and free from corrosion. Replace any damaged or corroded connectors. Think of it like tuning up your car — keeping everything in good working order ensures optimal performance and prevents future problems. Speaking of connections, make sure you are making good connections and don't have any loose wires. Loose connections increase resistance and are a fire hazard!
Finally, consider using dedicated circuits for high-power appliances. This prevents them from drawing excessive current from shared circuits, which can lead to significant voltage drop. It's like giving each appliance its own personal power lane, ensuring that it gets all the juice it needs without affecting other devices. Implementing these strategies will help you minimize voltage drop and optimize the performance and safety of your electrical system. You might even find that your lights are brighter, your appliances run smoother, and your overall electrical experience is much more enjoyable.

Voltage Drop FAQs
5. Got Questions? We've Got Answers!
Still have questions about voltage drop? No problem! Here are some frequently asked questions to clear up any remaining confusion.
Q: What happens if voltage drop is too high?
A: Excessive voltage drop can lead to a variety of problems, including dim lights, malfunctioning appliances, overheated motors, and even fire hazards. Basically, your electrical equipment won't perform as expected and could be damaged.
Q: How do I measure voltage drop?
A: You can measure voltage drop using a multimeter. Measure the voltage at the source (e.g., the breaker panel) and then measure the voltage at the load (e.g., an appliance). The difference between the two readings is the voltage drop.
Q: Is voltage drop always a bad thing?
A: While significant voltage drop is undesirable, a small amount of voltage drop is unavoidable. The goal is to keep it within acceptable limits, typically around 3% for branch circuits and 5% for feeders.
Q: Can voltage drop affect my energy bill?
A: Yes, excessive voltage drop can lead to inefficiencies in your electrical system, causing appliances to draw more power than they need to perform their tasks. This can result in higher energy bills. So keeping those voltages in check can help keep costs down!
Q: Does aluminum wire have more voltage drop than copper?
A: Generally, yes. Aluminum has higher resistance compared to copper for the same wire size. That's why for equal applications an aluminum wire needs to be a larger gauge than copper to carry the same load with acceptable voltage drop. It also comes with it's own set of safety concerns if not installed properly, so it's best to consult a professional when dealing with aluminum wiring.