Smart Tips About What Is The Bus System In Electrical
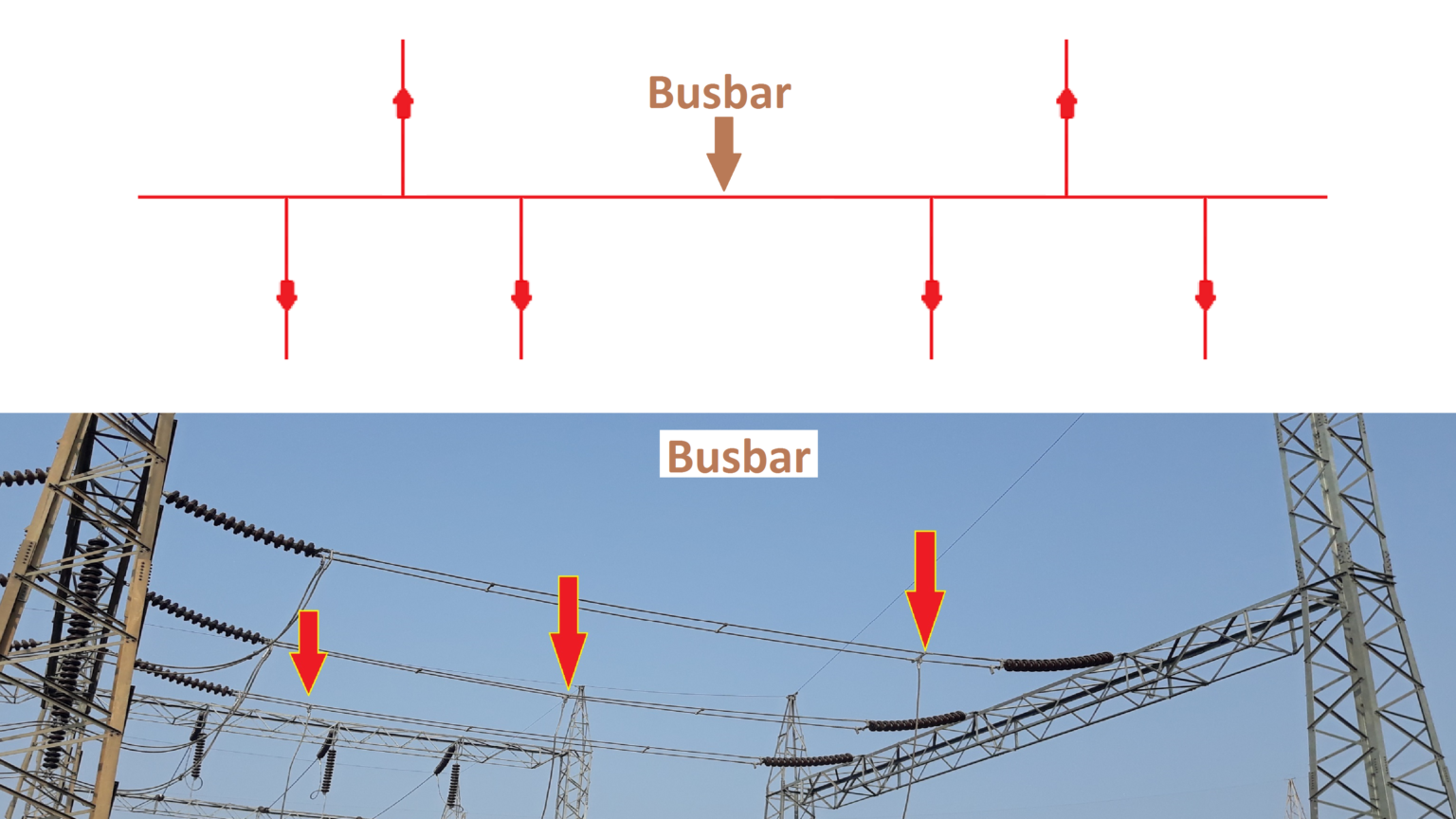
What Is A Electrical Bus Bar At Sue Alexander Blog
Unveiling the Mystery of the Electrical Bus System
1. What Exactly Is This Electrical Bus Thingy?
Okay, let's get one thing straight. We're not talking about the yellow school bus that tormented you every morning with its ear-splitting brakes and questionable seat cushions. This "bus" is a totally different beast. In the world of electricity, a bus system is essentially a network of conductors that act as a central hub for distributing power. Think of it as the Grand Central Station of electricity, where power from various sources arrives and then gets dispatched to different destinations.
Imagine a power plant generating electricity. That electricity needs to get to your house to power your lights, TV, and, most importantly, your coffee maker. The bus system is a critical part of that journey. It's a common point where the power source connects, and from there, it gets distributed to various loads or circuits. So, without this clever bit of engineering, your life would be significantly less caffeinated.
This electrical bus system comes in different shapes and sizes. It can be anything from a simple copper bar in a small circuit breaker panel to a complex network of conductors in a massive power substation. The size and complexity depend on the amount of power being distributed and the number of circuits being served. No matter the size, the fundamental purpose remains the same: to efficiently and reliably distribute electrical power.
Think of it this way: If your home electrical panel is the local distribution hub, then a large power substation is like the regional distribution center. Both are bus systems, just operating on vastly different scales. The key is that they provide a common connection point and a pathway for electricity to flow from the source to the loads that need it. Essentially, it's the electrical equivalent of a well-organized highway system ensuring the smooth flow of power across the network.

Electric Vehicle Bus Vehcile Architecture Hvg Jen Kaycee
The Backbone of Power Distribution
2. Why Can't We Just Wire Everything Directly?
Now, you might be thinking, "Why all this fuss about a bus system? Why can't we just run wires directly from the power source to each device?" Good question! The answer lies in efficiency, safety, and flexibility. Imagine trying to connect every appliance in your house directly to the power plant. It would be a tangled mess of wires, incredibly inefficient, and a potential fire hazard waiting to happen.
The bus system provides a much more elegant and practical solution. It allows you to connect multiple circuits and devices to a single point, simplifying the wiring and reducing the overall complexity. Furthermore, it makes it easier to protect the circuits with circuit breakers or fuses. If a fault occurs in one circuit, the breaker trips, isolating the problem without disrupting the power supply to the other circuits.
Flexibility is another crucial benefit. As your electrical needs change — maybe you decide to add a new room or install a fancy hot tub — it's much easier to add new circuits to an existing bus system than to run completely new wires from the power source. This modularity makes the bus system a scalable and adaptable solution for power distribution.
Consider a scenario where you have several machines in a factory that need varying amounts of power at different times. A bus system allows you to allocate power efficiently to each machine as needed, ensuring that no machine is starved of power while others are unnecessarily overloaded. This balanced distribution optimizes energy usage and prevents potential equipment damage.
Types of Bus Systems
3. So, What Flavors Does This Bus Come In?
Like ice cream, bus systems come in different flavors, each designed to meet specific needs. Some of the most common types include single bus, double bus, and ring bus systems. The choice of which type to use depends on factors such as the reliability requirements, the load capacity, and the cost considerations.
A single bus system is the simplest and most economical option. It consists of a single busbar to which all incoming and outgoing circuits are connected. While it's cost-effective, it's also the least reliable. If the bus fails, the entire system goes down. Its fine for smaller applications where short outages are acceptable, but you wouldn't want it powering a hospital.
A double bus system offers improved reliability. It has two busbars, allowing you to switch circuits from one bus to the other in case of a fault. This provides redundancy and minimizes downtime. It's like having a backup generator, but for your entire electrical system.
The ring bus system takes reliability to the next level. The bus is arranged in a closed loop, so power can flow in either direction. If a section of the bus fails, power can still reach all the circuits from the other direction. This configuration is often used in critical applications where uninterrupted power supply is essential, such as data centers and hospitals. Essentially, this setup ensures that power always finds a way, like a persistent telemarketer. You can't get rid of it!

Electric Bus Diagram
Components of a Bus System
4. More Than Just a Wire
A bus system isn't just a single wire or bar. It's a collection of components that work together to ensure efficient and safe power distribution. These components include busbars, insulators, circuit breakers, and protective relays. Each plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the system.
Busbars are the heart of the system, providing the conductive path for the electricity to flow. They are typically made of copper or aluminum due to their high conductivity. Insulators are used to support the busbars and prevent them from coming into contact with grounded structures. These are essential for safety and preventing short circuits.
Circuit breakers are the unsung heroes of the electrical world. They protect the circuits from overloads and short circuits by automatically interrupting the flow of current when a fault occurs. They're like the bouncers of the electrical party, kicking out troublemakers before they can cause any serious damage.
Protective relays are sophisticated devices that monitor the electrical parameters of the system, such as voltage and current. If they detect an abnormal condition, they send a signal to the circuit breakers to trip, isolating the faulty section of the system. They act as the early warning system, alerting the system to potential problems before they escalate into major failures. They are the detectives of the electrical world, always on the lookout for suspicious activity.

Platform For Fully Electric Buses Motor Engineering
Maintaining Your Bus System
5. A Little TLC Goes a Long Way
Like any other electrical equipment, bus systems require regular maintenance to ensure their reliability and longevity. This includes visual inspections, cleaning, and testing. Neglecting maintenance can lead to corrosion, loose connections, and ultimately, system failures.
Visual inspections are the first line of defense. Look for signs of corrosion, overheating, or physical damage. Loose connections can cause arcing and overheating, which can lead to fires. Tighten any loose connections and replace any damaged components.
Cleaning is also important. Dust and dirt can accumulate on the busbars and insulators, reducing their insulating properties and increasing the risk of short circuits. Use a non-conductive cleaner to remove any dirt or debris.
Testing involves using specialized equipment to verify the electrical integrity of the system. This includes insulation resistance tests and contact resistance tests. These tests can identify potential problems before they cause a failure, allowing you to take corrective action and prevent costly downtime. Think of it as a regular check-up for your electrical system.
